
Hope that you now can understand the basic difference between the two instructions. Use the RUN instructions with regular Linux commands for downloading and extracting files. Try and avoid using ADD wherever possible. So if you just want to copy files or directories, you should use the COPY instruction alone. Differences between COPY and ADD Dockerfile Instructions The corresponding instruction would be: COPY /home/user/application /opt/appĪs best practice, the developers at Docker officially recommend using the above instruction to avoid confusion. So, it is basically the first point in the ADD instruction section that was discussed above. Its function is just one - copy files or directories from the source location on the host to the destination location on the Docker image.

The COPY instruction is an evolution of the ADD instruction that was designed to mitigate confusion among Docker users.
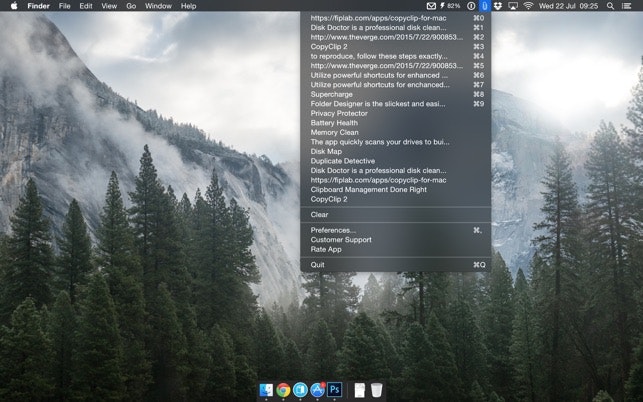
#Copyclip instructions pdf#
While building your Docker image, you can use the following instruction to download a file and store it a desired location on your container image: ADD /home/userĪfter the image is built, you can have this PDF document beforehand you launch a container based on it. It is similar to how wget -P works but for Dockerfiles. The behaviour is similar to what happens when you use the tar command to extract a tarball to a specific directory on your host system. The contents are unpacked as a directory inside the destination location of the Docker image you build.
You can also use the ADD instruction to extract compressed archives with formats - identity, gzip, bzip2 or xz. It is not going to copy the application directory itself. Here, only the contents of the /home/user/application directory is copied into /opt/app including its metadata. Say for example, if you want to copy local files on the host system from /home/user/application into /opt/app on your Docker image, you can include the following instruction inside your Dockerfile: ADD /home/user/application /opt/app Copying of local files into the container image The ADD instruction has the following three capabilities: 1. COPY can only copy the files and direcories. This is the reason why COPY is recommended these days and you'll find ADD only in older tutorials and documentations.ĪDD is older instruction that can download and extract files apart from copying them to the images from host. For downloading and extracting files, regular Linux commands like curl and tar are used with the RUN instructions. The focus is on providing a simple, straightforward and more streamlined command structure.ĬOPY was introduced as a straightforward replacement to ADD. If ADD can do all this, why do we have COPY? It's because the Docker commands have been restructured several times so far.
#Copyclip instructions archive#
This also creates a problem sometime if ADD could not support the archive format. It can also extract compressed files assuming that it supports the archive format. The ADD instruction is relatively older and is capable of more tha just copying files and directories. Dockerfile ADD vs COPYīoth ADD and COPY are designed to add directories and files to your Docker image. They have similar goals but in terms of behavior, they are different. Why does Dockerfile have two commands for the same task? Is there a difference between the two? Indeed. Then you come across COPY and ADD and realize that both instructions do the same job copy the files and directories to your modified Docker image from the host. You come across a variety of Dockerfile instructions like FROM, RUN etc. You are new to Docker and you are learning to create custom Docker images using Dockerfile.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
